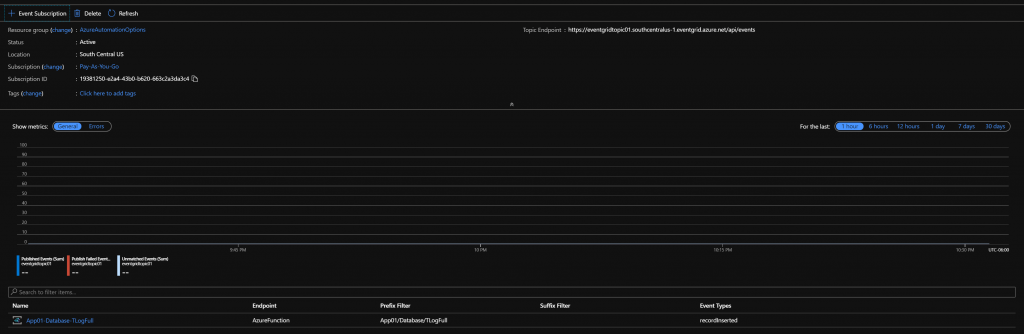
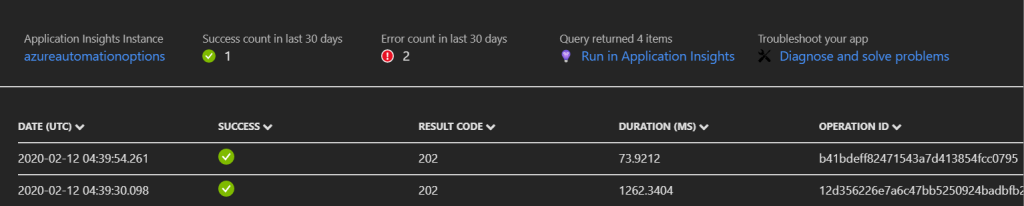
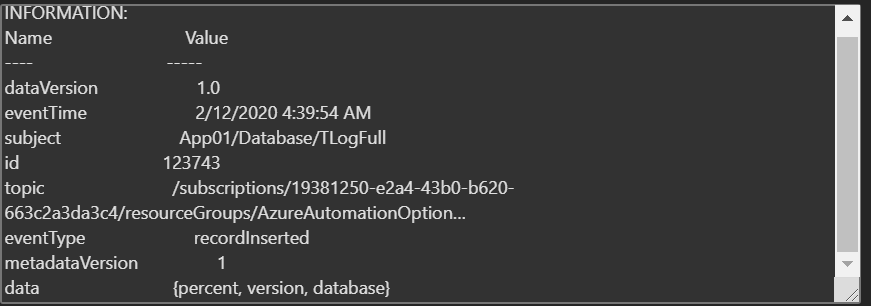
This is a continuation of the blog series that fellow MVP Billy York and I are putting on around the journey from on-prem SCORCH to Automation in Azure. In this post we will look at a new preview Log Analytics solution that will help you monitor and respond to issues that will invariably happen with Logic Apps.
Logic App Management allows heavy users of Logic Apps to get both ‘at-a-glance’ updates on the success or failure of their apps, or drill down deeply into app runs and get details such as start/stop time, execution duration, action durations, etc… It is especially useful when you have a very large set of Logic Apps. Trying to get a single pane of glass when you have dozens or hundreds of Logic Apps is difficult with this exciting preview feature.
To add this solution to Log Analytics, you will need…..wait for it…..a Log Analytics workspace! Your existing Log Analytics workspace will do just fine – no need to create a new one. In fact, there are a lot of reasons why you wouldn’t want to! Once you have an eligible workspace, it’s time to add the solution. You can get to this either by adding a resource to the resource group, or adding the solution directly from the workspace – both will start same wizard
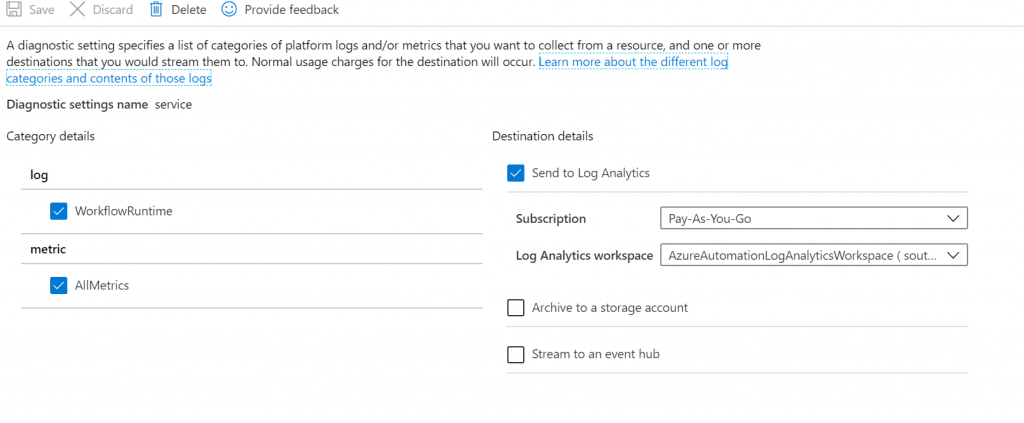
The actual wizard is very simple – just pick your workspace and click create. Once you have your solution provisioned, you can turn it on or off per Logic App by selecting the “Diagnostic Settings” on the LA and editing the setting below – if you want to turn it off, just uncheck the “Send to Log Analytics” setting.

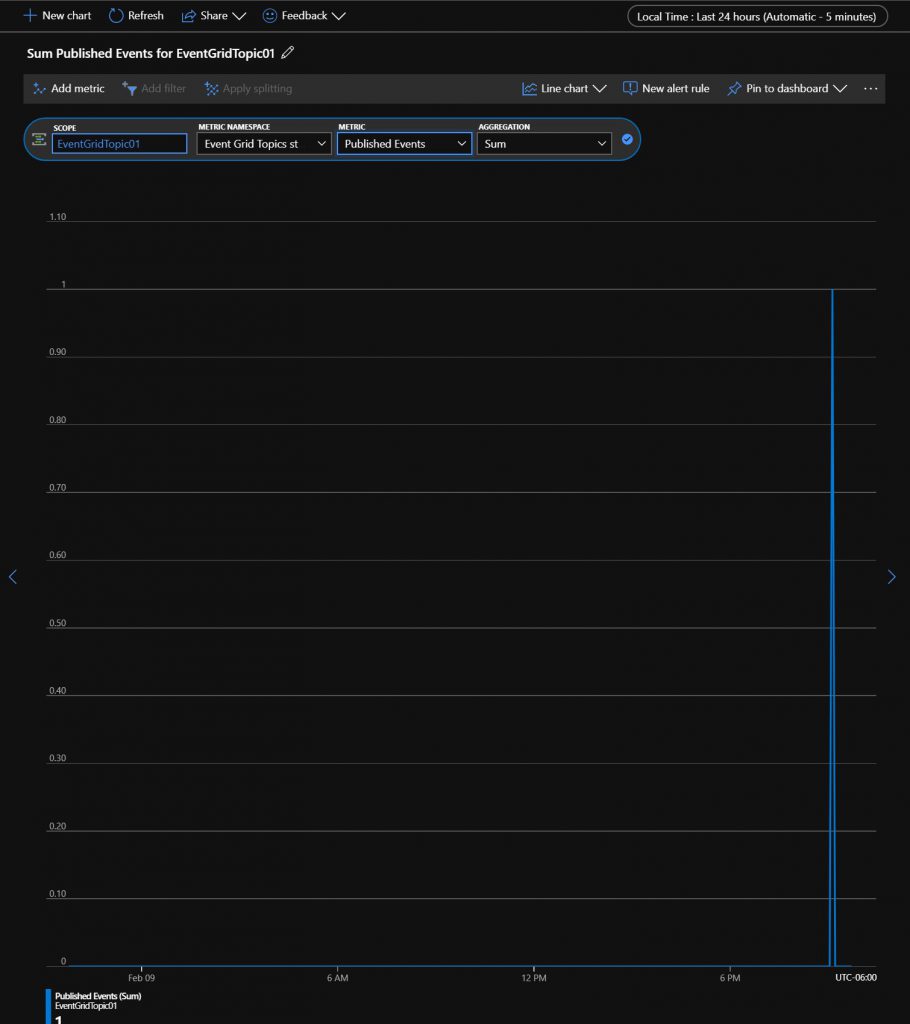
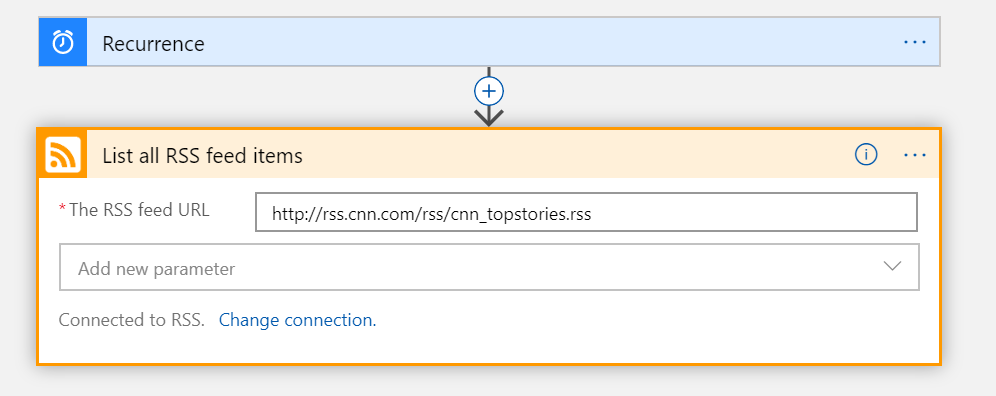
For this article, I setup a couple of simple Logic Apps – both of them query RSS feeds, but one has a good feed URL, and the other doesn’t. I varied their start times a bit just to show some contrasting data.
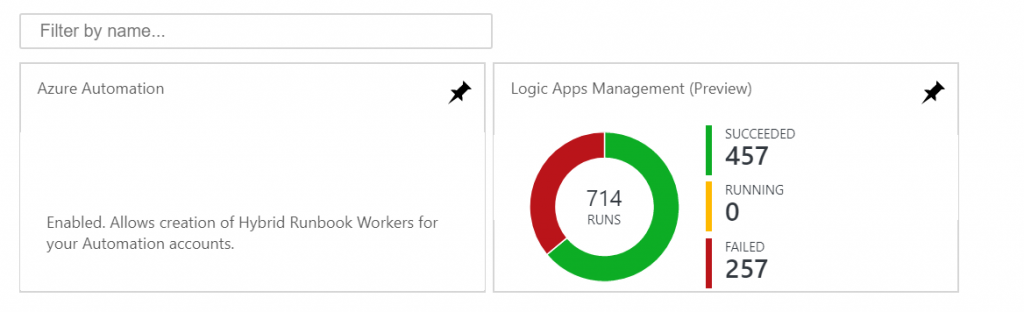
I let these apps run for a couple of days. When I look at my Log Analytics workspace, I am greeted with this new tile, and can drill down into to get a nice Logic App run overview:
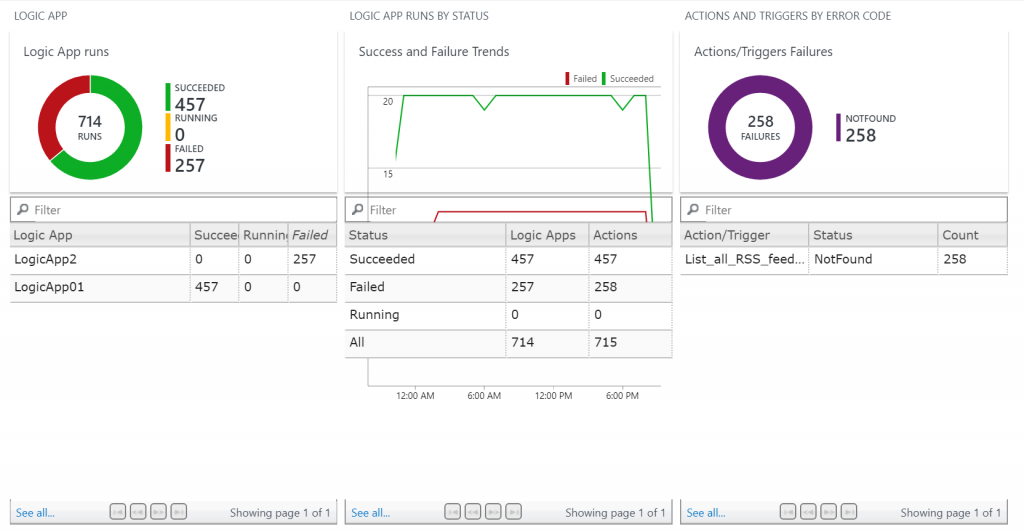
This is a great overview screen for your apps. Notice that the central graph is slightly off – I have tried it in multiple browsers on multiple themes, but it shows the same in each. Hence the ‘preview’ moniker on the solution, I guess. Regardless, at a simple glance I can see the LAs that have succeeded or failed, get a list of the errors, and see a visual comparison of the status of my apps. Clicking on the ‘runs’ tab brings me to a bit more details, and if I click on the “See All” link in the bottom left of each tile, I get a familiar looking interface 🙂
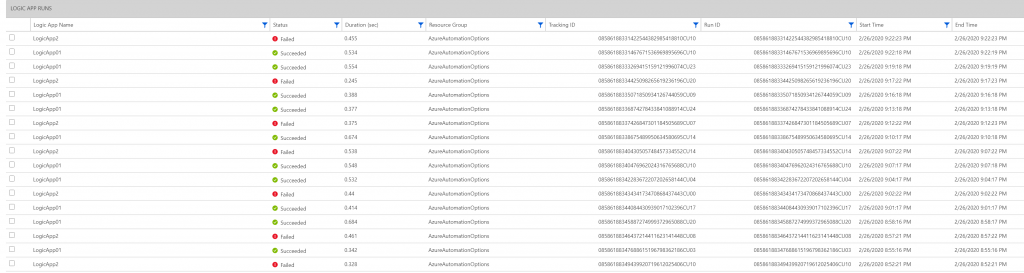
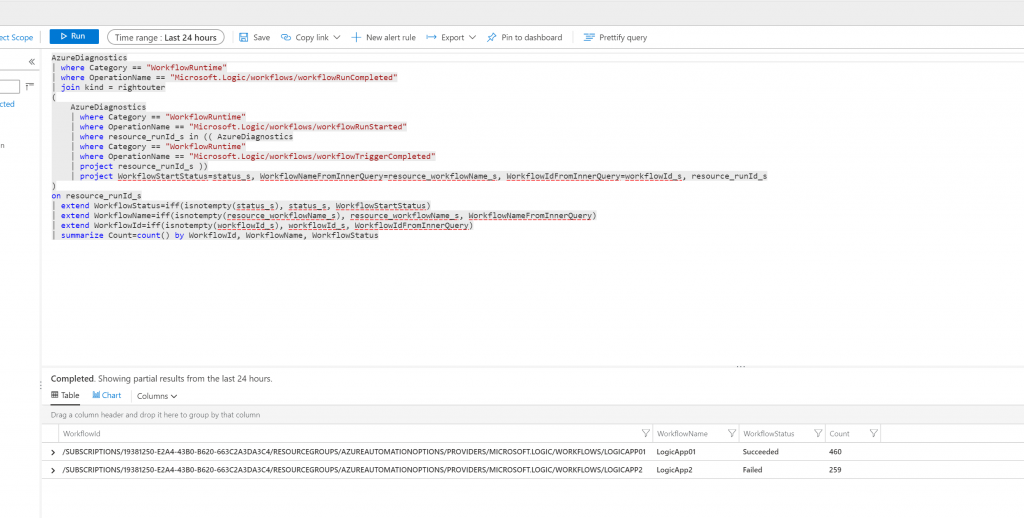
For anyone wanting to know the actual query, here it is:
AzureDiagnostics
| where Category == "WorkflowRuntime"
| where OperationName == "Microsoft.Logic/workflows/workflowRunCompleted"
| join kind = rightouter
(
AzureDiagnostics
| where Category == "WorkflowRuntime"
| where OperationName == "Microsoft.Logic/workflows/workflowRunStarted"
| where resource_runId_s in (( AzureDiagnostics
| where Category == "WorkflowRuntime"
| where OperationName == "Microsoft.Logic/workflows/workflowTriggerCompleted"
| project resource_runId_s ))
| project WorkflowStartStatus=status_s, WorkflowNameFromInnerQuery=resource_workflowName_s, WorkflowIdFromInnerQuery=workflowId_s, resource_runId_s
)
on resource_runId_s
| extend WorkflowStatus=iff(isnotempty(status_s), status_s, WorkflowStartStatus)
| extend WorkflowName=iff(isnotempty(resource_workflowName_s), resource_workflowName_s, WorkflowNameFromInnerQuery)
| extend WorkflowId=iff(isnotempty(workflowId_s), workflowId_s, WorkflowIdFromInnerQuery)
| summarize Count=count() by WorkflowId, WorkflowName, WorkflowStatusThe benefits of having this data in the “Gateway Drug” (trademark pending) of Azure – Log Analytics – should be obvious. Want to export your Logic App data to PowerBI, or even better setup alerts when a LA fails? Combine your LA data with feeds from AAD, Graph, Office365, etc…. Having all of this data in an easily queried repository is priceless.